An effective annual yield is defined as the total profit or returns on a bond that an investor receives. An effective annual yield differs from nominal yield or coupon rate on a bond. For example, an investor purchased a $1000 bond, with 5% interest per year with a semi-annual payment. The effective annual yield ends up being more than the nominal yield, and it is a more accurate indicator of how much is actually earned from the bond.

It is the amount actually received from bonds when the dividends are reinvested, in other words, it takes into account the power of confounding interest, as it builds over time. The effective yield is the return on a bond that has its interest payments (or coupons) reinvested at the same rate by the bondholder. Effective yield is the total yield an investor receives, in contrast to the nominal yield—which is the stated interest rate of the bond’s coupon. Effective yield takes into account the power of compounding on investment returns, while nominal yield does not.
What is the Effective Annual Interest Rate?
Effective yield is one way that bondholders can measure their yields on bonds. There’s also the current yield, which represents a bond’s annual return based on its annual coupon payments and current price, as opposed to the face value. First Federal is offering an annual interest rate of 7.20%, while Second National Bank is offering a rate of 7.00% with daily compounding. To make a fair comparison, the Second National Bank needs to be converted into an effective yield. When banks are charging interest, the stated interest rate is used instead of the effective annual interest rate. This is done to make consumers believe that they are paying a lower interest rate.
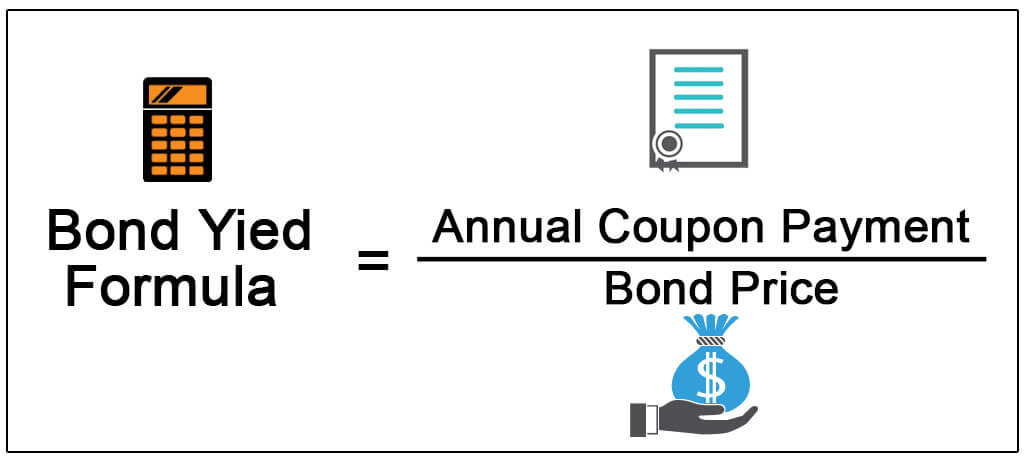
Where EAY is the effective annual yield, HPR is the holding period return and t is the number of days for which holding period return is calculated. Effective annual yield is a measure of annual return on investment that takes the compounding of interest into account. It is calculated by compounding and annualizing the holding period return. The term effective interest rate is used to describe the actual rate of interest received when compounding is applied to a nominal rate of interest. The effective interest rate is useful when evaluating alternatives involving various nominal rates applied to different compounding periods. Effective annual yield is a measure of the actual or true return on investment.
What Is the Effective Yield?
Gordon Scott has been an active investor and technical analyst or 20+ years.
Form 424B2 BANK OF NOVA SCOTIA – StreetInsider.com
Form 424B2 BANK OF NOVA SCOTIA.
Posted: Thu, 03 Aug 2023 15:24:32 GMT [source]
Certain kinds of investments are particularly well suited to helping investors take advantage of long-term growth trends. The effective yield will be the absolute increase as a percentage of the principal invested. For the Level II exam, I endeavoured not to repeat the mistakes I made.
Effective Annual Yield Calculator
The effective annual rate calculator is an easy way to restate an interest rate on a loan as an interest rate that is compounded annually. Effective annual rate (EAR), is also called the effective annual interest rate or the annual equivalent rate (AER). The effective annual yield shows how much a bond will actually earn when the dividends are reinvested.
- For example, a semi-annual coupon frequency means that you will receive two coupon payments in a year.
- One method of expressing yield (annualised), assuming compound interest.
- Over the course of 10 years, reinvesting the dividends gives a total of $7573.
- I love the CFA Program and truly value the skills and ethics that are imparted to make me a better finance professional.
One method of expressing yield (annualised), assuming compound interest. It is based on information and assumptions provided by you regarding your goals, expectations and financial situation. The calculations do not infer that the company assumes any fiduciary duties. The calculations provided should not be construed as financial, legal or tax advice. In addition, such information should not be relied upon as the only source of information. This information is supplied from sources we believe to be reliable but we cannot guarantee its accuracy.
How to calculate the effective annual yield? Effective annual yield formula
Hypothetical illustrations may provide historical or current performance information. We realise some candidates prefer to purchase courses as they need individually, so we endeavour to give more options to our potential students. Check out our Udemy Courses Page to find out which of our courses are available on Udemy for your purchase. For those of you who are new to Udemy, it is the world’s largest marketplace for online courses.
When compounding is applied, the effective rate of interest paid will always be higher than the nominal rate applied. Effective yield is useful when you are considering various investment options where the interest rates are expressed at different compounding rates. In such a situation, you can convert all the rates into effective annual yields and then make an informed decision. The difference between the two is that the nominal rate does not take compounding into consideration, while the effective annual yield does. The Effective Annual Interest Rate (EAR) is the interest rate that is adjusted for compounding over a given period.
The amount of interest received is called the nominal yield and it is how much is earned from the bond. Often investors will reinvest the interest received, to immediately purchase more bonds. Since more money has been put into the bonds, more money from the interest is received in the following payments. This means that the actual amount earned from the bond is more than the nominal yield would initially indicate. The amount actually received is referred to as the effective annual yield.
Based on the Pareto 80/20 principle, I learnt to extract the most essential bits from the curriculum enough to give me that 80% result to pass. Instead of reserving huge segments of time to study, I carved out pockets of time to learn and practise – accommodating to my full-time job. I managed to pass my Level II and Level III exams consecutively with considerably less effort and stress than when I did my level I. A bond is a debt security, usually issued by a government or a corporation, sold to investors. The investors will lend the money to the bond issuer by buying the bond.
What Is APY and How Is It Calculated With Examples – Investopedia
What Is APY and How Is It Calculated With Examples.
Posted: Sat, 25 Mar 2017 18:48:27 GMT [source]
It is the last payment a bond investor will receive if the bond is held to maturity. Our mission is to produce effective learning materials and to present them in a way that is suitable for busy professionals to consume in their pockets of time. PrepNuggets is a creator of CFA® program study materials to aid candidates who are looking for more concise materials for their exam preparation. All materials are crafted in-house by founder and chief instructor Keith Tan.
These are typically corporations, cities, and the United States government. An initial amount, or the principal, is paid back to the bondholder at the end of the issue period. Before the payback date, there are set periods when interest is paid to the investor. The stated annual interest rate and the effective interest rate can be significantly different, due to compounding. The effective interest rate is important in figuring out the best loan or determining which investment offers the highest rate of return. As Bond A pays coupons semi-annually, its coupon frequency is 2, and this is a number you need to put in the effective annual yield formula in the next step.
Effective Annual Rate Calculation:
For example, for a loan at a stated interest rate of 30%, compounded monthly, the effective annual interest rate would be 34.48%. Banks will typically advertise the stated interest rate of 30% rather than the effective interest rate of 34.48%. Both Bond A and Bond B have an effective annual yield of 5.6%, so they each have the same yield. Note that since Bond A is paid once a year, the effective annual rate is the same as the nominal or coupon rate. The drawback of using the effective yield is that it assumes that coupon payments can be reinvested in another vehicle paying the same interest rate. This is not always possible, considering the fact that interest rates change periodically, falling and rising due to certain factors in the economy.
- For example, the EAR of a 1% Stated Interest Rate compounded quarterly is 1.0038%.
- The bigger your investment base, the more that time and math will conspire to build up your wealth.
- The amount actually received is referred to as the effective annual yield.
- Long-term investors seek to build portfolios that will gain maximum value over time.
If you don’t have a high tolerance for risk, you might want to consider a money market fund. A money market fund is one that invests in low-risk government securities such as Treasury bills and commercial short-term loans. Unlike other bank or credit union investments such as certificates of deposit, money market funds are not federally insured and can change in price. Money market funds are highly liquid (meaning they can be converted to cash). So based on nominal interest rate and the compounding per year, the effective rate is essentially the same for both loans. Consider an investment of $100 at a nominal rate of 10% compounded monthly.